Frequently Asked Questions
How do I find out which compute platforms and software are available at GACRC?
A list of GACRC systems, including a brief description of the compute platforms, is available at the Systems page.
Over 700 applications and software packages are available on GACRC machines. We do not have a comprehensive list of all of them here, but most open-source or free software packages compatible with 64-bit CentOS Linux OS can be installed on the clusters. A few of them are listed in the Software page.
How do I apply for accounts on GACRC machines?
User accounts are created as part of a "lab group" which has been registered by a Principal Investigator (PI), i.e. a UGA faculty. Once the group is registered, the PI will receive an email stating that he/she can request individual accounts for members of his/her group. For more information, please see http://gacrc.uga.edu/accounts
How do I connect to a GACRC machine?
Users can access GACRC machines using secure shell (ssh) from their local machines either on-campus or off-campus. To connect via ssh, you must have an ssh software on your local machine and a connection to the UGA campus network. ssh software is included in recent releases of Unix based operating systems (including Linux and Mac OSX). If you are using a Windows computer, you can download and install PuTTY. You can find detailed instructions on how to download and install PuTTY on your Windows computer at https://wiki.gacrc.uga.edu/wiki/How_to_Install_and_Configure_PuTTY
For more detailed information on how to connect to a specific GACRC machine, please see the Connecting page.
How do I copy files to/from a GACRC machine?
Users can transfer files between their local machines and GACRC machines using FTP with explicit SSL encryption, a secure copy (scp), WinSCP, FileZilla, etc. To transfer files using scp (or SSH file transfer) you must have scp (or SSH) on your local machine and a connection to the UGA campus network. An scp software is included in recent releases of Unix based operating systems (including Linux and Mac OS X). Two file transfer software that support FTP with explicit SSL encryption are the open source software FileZilla (available for Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux) and WinSCP (available for Windows machines).
For more detailed information on how to copy files to/from a specific GACRC machine, please see the Transferring Files page.
How do I print files that are on a GACRC machine?
Files on any GACRC machine cannot be directly printed on your local printer. Please transfer the files from the GACRC machine to your local machine (see question above) and print them from your local machine.
How do I run jobs on a GACRC machine?
Jobs should not be run on the login node of GACRC machines.
Sapelo2 uses the Slurm queueing system, which should be used for both interactive and batch jobs. For more information, please see the Running Jobs on Sapelo2 page.
The teaching cluster uses the Slurm queueing system too, which should be used for both interactive and batch jobs. For more information, please see the Running Jobs on the teaching cluster page.
How do I change my default shell on a given machine?
When you login to an GACRC machine, the environment on your terminal and the commands that you type at the prompt are defined/interpreted by a program called shell. Examples of shell are bash, csh, ksh, tcsh, zsh. The syntax for setting environment variables and some of the functionality of your keyboard depend on the shell that you are running. For example, with bash and tcsh it is straightforward to use up arrows to recover previous commands. All users have a default shell (bash) defined at account creation time. Users who wish to have their default shell changed can request that via the GACRC General Support.
Can I use text files (programs, scripts, etc) created on a Windows machine on the GACRC Unix/Linux machines?
Text (ascii) files created on Windows machines might have Windows newlines that are not interpreted correctly by a Unix/Linux system. However, you can convert a Windows text file to the Unix/Linux format with the dos2unix command available on the GACRC's Sapelo2 and the teaching cluster. The syntax is
dos2unix filename
where filename is the name of the ascii file (such as program.c, program.f, run.sh, input.txt, etc) created on a Windows machine.
Can I use text files (programs, scripts, etc) created on a Mac machine on the GACRC Unix/Linux machines?
Text (ascii) files created on Mac machines might have Mac newlines that are not interpreted correctly by a Unix/Linux system. However, you can convert a Mac text file to the Unix/Linux format with the mac2unix command available on the GACRC's Sapelo2 and the teaching cluster. The syntax is
mac2unix filename
where filename is the name of the ascii file (such as program.c, program.f, run.sh, input.txt, etc) created on a Mac machine.
How do I forward X Window applications running on GACRC machines to my Windows desktop?
A number of software installed on GACRC machines have X Window (GUI) front ends. Examples of such applications are Matlab, Maple, some text editors and debuggers, etc. In order to export such X Window applications to your Windows desktop, your desktop needs to have an X Window client (or server) running on it. A free X Window server for Microsoft Windows (10/8/7) is Xming. You can download it from Sourceforge and make a default installation. You will need to install the Xming server and the Xming-fonts package. Some applications also require having Xming-mesa installed. During the installation of Xming, you might want to select the option to create a desktop icon for Xming. When the installation of these two packages is complete, double click on the Xming icon to start the X Window server (a capital X will appear on your task bar).
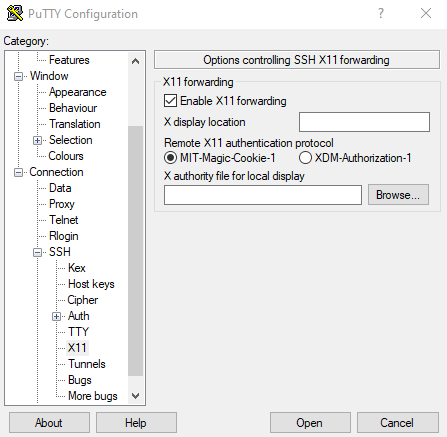
Now you need to configure your SSH client to allow tunneling of X11 connections. For example, if you use PuTTY you need to open it, expand the SSH option in the left pane, click X11 in the left pane, and check the "Enable X11 forwarding" box.
Once that is done, you can SSH into your GACRC account (e.g. Sapelo2 account) and run X Window applications. The application should appear on your local Windows desktop. Each time you logout and log back into your Windows desktop, you would need to start the Xming Server manually before using PuTTY to connect to your GACRC account.
How do I forward X Window applications running on GACRC machines to my Mac?
For Apple's OSX v10.6.3 and beyond, users have to manually install XQuartz to enable the X11 features according to Apple. It is free and available at XQuartz.
Then connect to Sapelo as:
ssh -X myid@sapelo2.gacrc.uga.edu
Please check where your local machine has xauth installed, e.g. is it in /opt/X11/bin/xauth or somewhere else? Then edit the ~/.ssh/config file on your local machine (not on Sapelo2) to add the location of xauth, e.g. add
Host * XAuthLocation /opt/X11/bin/xauth
if that is the path of xauth on your machine. If ~/.ssh/config does not exist, create this file and put the lines above in this file.
After making this change on your local machine, start an XQuartz terminal and connect to sapelo2 with the ssh -X command above.
How to retrieve data from NCBI?
Please contact us to get permission if you need to connect to NCBI on GACRC clusters. Please specify your path of scripts, the block of code on how to connect to NCBI and command to test your script in the request.
NCBI offers e-utilities to fetch data from their website: NCBI Eutility
Detailed information on how to connect to NCBI is at NCBI Connection
How do I acknowledge the GACRC in my publication?
A sample acknowledgment statement is provided at http://gacrc.uga.edu/about/acknowledgment-statement