Available Toolchains and Toolchain Compatibility: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
!Intel Compiler (icc, icpc, ifort) | !Intel Compiler (icc, icpc, ifort) | ||
! scope="col" width="100px" |MPI library | ! scope="col" width="100px" |MPI library | ||
! scope="col" width="100px" |MKL | ! scope="col" width="100px" |MKL, FFT | ||
|- | |- | ||
<!--LIST BEGIN-->|- | <!--LIST BEGIN-->|- | ||
| Line 66: | Line 65: | ||
|impi/2021.4.0 | |impi/2021.4.0 | ||
|imkl/2021.4.0 | |imkl/2021.4.0 | ||
imkl-FFTW/2021.4.0 | |||
|- | |- | ||
|2021a | |2021a | ||
| Line 73: | Line 72: | ||
|impi/2021.2.0 | |impi/2021.2.0 | ||
| imkl/2021.2.0 | | imkl/2021.2.0 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|2020b||GCC/10.2.0 | |2020b||GCC/10.2.0 | ||
| Line 90: | Line 88: | ||
|intel-compilers/2021.4.0 | |intel-compilers/2021.4.0 | ||
|impi/2021.4.0 | |impi/2021.4.0 | ||
| rowspan="4" | | | rowspan="4" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 13:33, 5 September 2023
We use EasyBuild to build most of the software modules on the Sapelo2 cluster. Easybuild is a software build and installation framework that allows us to manage scientific software on High Performance Computing (HPC) systems in an efficient way. EasyBuild employs so-called compiler toolchains or, simply toolchains for short, in handling the build and installation processes. A typical toolchain consists of one or more compilers, usually put together with some libraries for specific functionality, e.g., for using an MPI stack for distributed computing, or which provide optimized routines for commonly used math operations, e.g., the well-known BLAS/LAPACK APIs for linear algebra routines. For detailed info about EasyBuild and its toolchains, please refer to EasyBuild and toolchains
Available foss and intel toolchains on Sapelo2
| Name | Version | Compiler(s) | MPI library | Linear algebra library | FFT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| foss | 2022a | GCC/11.3.0 | OpenMPI/4.1.4 | FlexiBLAS/3.2.0, ScaLAPACK/2.2.0 | FFTW/3.3.10, FFTW,MPI/3.3.10 |
| 2021b | GCC/11.2.0 | OpenMPI/4.1.1 | FlexiBLAS/3.0.4, ScaLAPACK/2.1.0 | FFTW/3.3.10 | |
| 2019b | GCC/8.3.0 | OpenMPI/3.1.4 | OpenBLAS/0.3.7, ScaLAPACK/2.0.2 | FFTW/3.3.8 | |
| gompi | 2022a | GCC/11.3.0 | OpenMPI/4.1.4 | ||
| 2021b | GCC/11.2.0 | OpenMPI/4.1.1 | |||
| 2019b | GCC/8.3.0 | OpenMPI/3.1.4 | |||
| GCC | 12.2.0, 11.3.0, 11.2.0, 10.2.0, 8.3.0 | ||||
| GCCcore | 12.3.0, 12.2.0, 11.3.0, 11.2.0, 10.2.0, 8.3.0 |
| Name | Version | GCCcore | Intel Compiler (icc, icpc, ifort) | MPI library | MKL, FFT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| intel | 2021b | GCC/11.2.0 | intel-compilers/2021.4.0 | impi/2021.4.0 | imkl/2021.4.0
imkl-FFTW/2021.4.0 |
| 2021a | GCC/10.3.0 | intel-compilers/2021.2.0 | impi/2021.2.0 | imkl/2021.2.0 | |
| 2020b | GCC/10.2.0 | iccifort/2020.4.304 | impi/2019.9.304 | imkl/2020.4.304 | |
| 2019b | GCC/8.3.0 | iccifort/2019.5.281 | impi/2018.5.288 | imkl/2019.5.281 | |
| iimpi | 2021b | GCC/11.2.0 | intel-compilers/2021.4.0 | impi/2021.4.0 | |
| 2021a | GCC/10.3.0 | intel-compilers/2021.2.0 | impi/2021.2.0 | ||
| 2020b | GCC/10.2.0 | iccifort/2020.4.304 | impi/2019.9.304 | ||
| 2019b | GCC/8.3.0 | iccifort/2019.5.281 | impi/2018.5.288 |
For a complete list of EasyBuild toolchains, please refer to List_of_known_toolchains
Toolchain compatibility
- Software modules built by EasyBuild generally have names in a format like Name/Version-Toolchain. When you load more than one software module built by EasyBuild, please make sure that all modules are built with the same or compatible toolchains. You can check this by looking into software modules' names. If you load more than one module and some toolchains are incompatible, you will end up with failing dependencies of Lmod errors, like this:
Lmod has detected the following error: These module(s) exist but cannot be loaded as requested
- Also please note that, when a conflicting module is loaded, one or more dependent modules of the software previously loaded could be replaced, and thus results in the software previously loaded being broken.
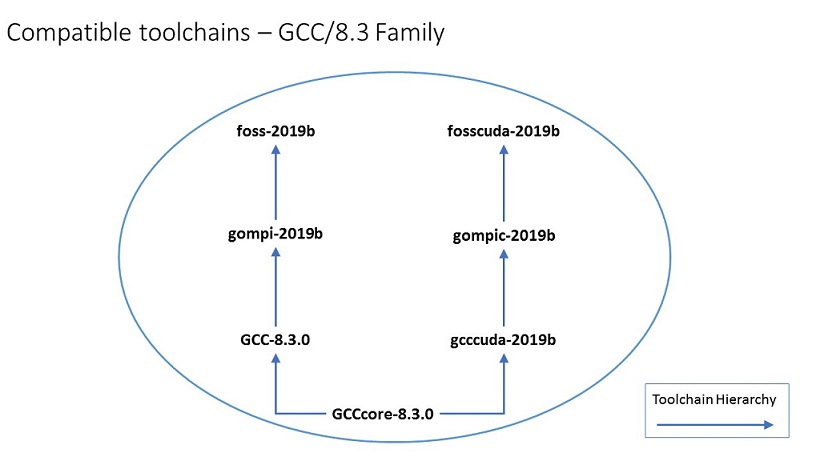
- The diagram below shows toolchains belonging to GCC/8.3.0 family. They are all compatible with each other. The blue connection lines with arrows illustrate toolchain build hierarchy, for example, GCC-8.3.0 is built on the top of GCCcore-8.3.0.
Dependency compatibility (to be added)
- The diagram below gives examples showing what will happen when incompatible toolchains and conflicting modules are loaded: