Using a Conda environment in Jupyter: Difference between revisions
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Conda environment == | == Conda environment == | ||
A Conda environment is a type of virtual environment. Conda environments are used to contain a set of software that you install (via Conda) into that environment | A Conda environment is a type of virtual environment. Conda environments are used to contain a set of software/packages that you install (via Conda) into that environment that may be accessed any time you activate the environment. To learn more about Conda environments, please see our wiki page on creating Conda environments '''[[Installing Applications on Sapelo2#How to install Conda packages|here]].''' | ||
== Open OnDemand == | == Open OnDemand == | ||
Open OnDemand is a web-based service that allows users to run software with a graphical user interface (GUI). Please see our wiki page on Open OnDemand [[OnDemand|'''here''']] to learn more. | Open OnDemand is a web-based service that allows users to run software with a graphical user interface (GUI) such as Jupyter Notebook. Please see our wiki page on Open OnDemand [[OnDemand|'''here''']] to learn more. | ||
== Using a Conda environment in Jupyter == | == Using a Conda environment in Jupyter == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
python -m ipykernel install --user --name=my_env | python -m ipykernel install --user --name=my_env | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Note: change my_env to whatever the name of your Conda environment is. | Note: change my_env to whatever the name of your Conda environment is. This is the name that you will see in Jupyter Notebook as an available kernel. | ||
=== Open Jupyter in Open OnDemand === | |||
Click on the Jupyter app in [https://ondemand.gacrc.uga.edu/ Open OnDemand] and choose your desired resources. Please ensure that you choose the Miniforge3 version of Jupyter. | |||
Click launch at the bottom of the page to start a Jupyter Notebook session. You will be redirected to "My Interactive Sessions" where you can wait for the job to be allocated resources.<br> | |||
[[File:Screenshot 2023-12-13 at 10.25.00 AM.png|alt=|border|700x700px]] | |||
Once the job starts, click on Connect to Jupyter. This will open Jupyter in a new page in your browser. | |||
'''For Jupyter versions < 7.0.0 please see below''' (for versions > 7.0.0, scroll down). | |||
From here, click "new" and you should see the name of the ipykernel you created. Clicking on that will start a Jupyter notebook with a kernel that has access to all of the packages in your Conda environment. | |||
[[File:Load_condakernel.png|alt=|border|1111x1111px]] | |||
'''For Jupyter versions > 7.0.0 please see below.''' | |||
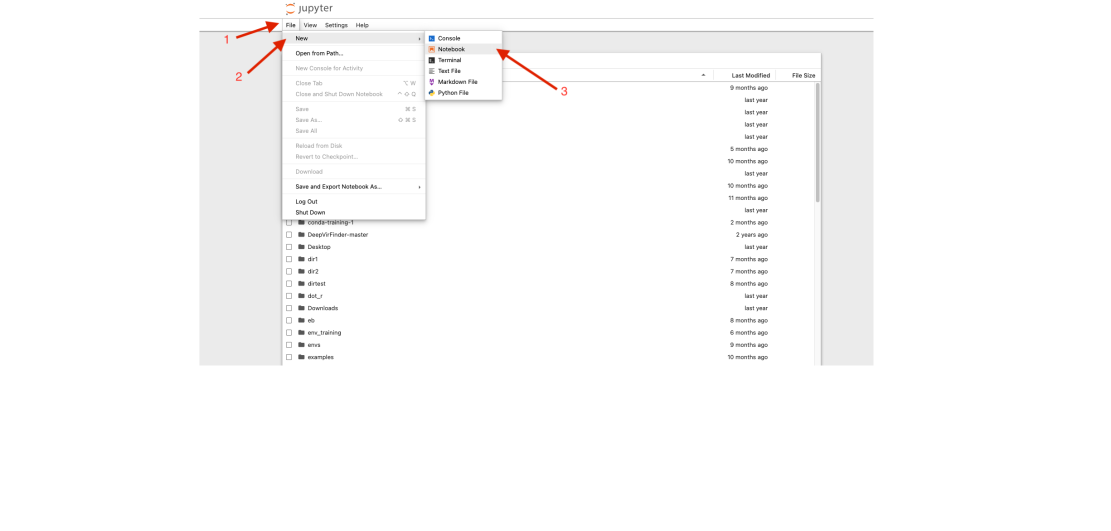
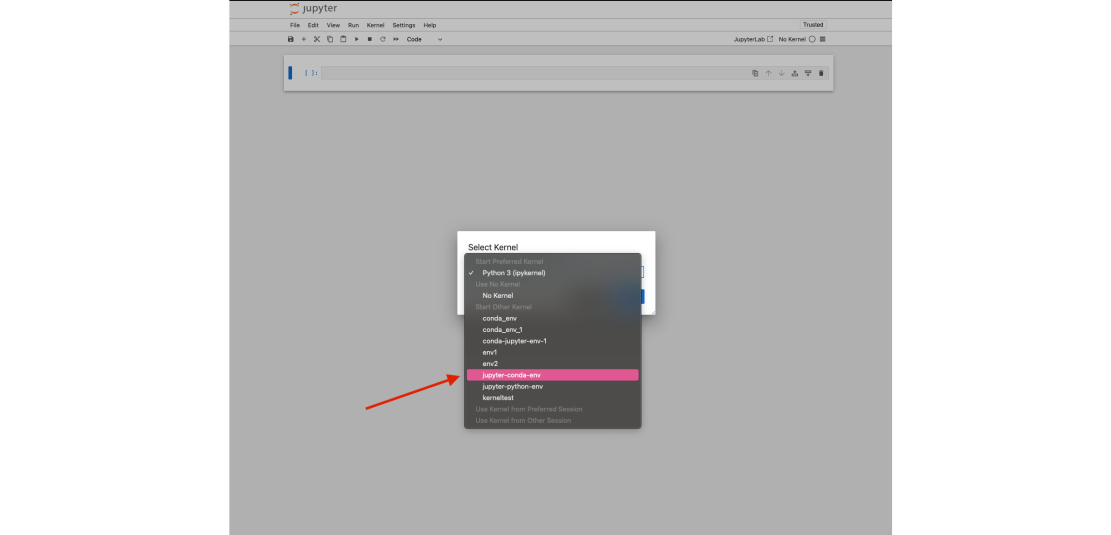
From here, click File > new > notebook. A new Jupyter notebook will open and a window will appear titled "Select Kernel". Click the drop down menu and under "Start Other Kernel" you should see the name of your Conda environment. Clicking on that will start your Jupyter notebook with a kernel that has access to all of the packages in your Conda environment. | |||
[[File:New-jupyter-interface.png|alt=|border|1111x1111px]] | |||
[[File:Load_new_condakernel.png|alt=|border|1111x1111px]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:40, 13 August 2025
Conda environment
A Conda environment is a type of virtual environment. Conda environments are used to contain a set of software/packages that you install (via Conda) into that environment that may be accessed any time you activate the environment. To learn more about Conda environments, please see our wiki page on creating Conda environments here.
Open OnDemand
Open OnDemand is a web-based service that allows users to run software with a graphical user interface (GUI) such as Jupyter Notebook. Please see our wiki page on Open OnDemand here to learn more.
Using a Conda environment in Jupyter
These steps will allow you to access the software you install into a Conda environment within Jupyter Notebook running on Open OnDemand
Create the Conda environment
Create your Conda environment and install any packages you will want to use.
Install ipykernel
While your Conda environment is still activated, install ipykernel to your Conda environment with:
conda install ipykernel python -m ipykernel install --user --name=my_env
Note: change my_env to whatever the name of your Conda environment is. This is the name that you will see in Jupyter Notebook as an available kernel.
Open Jupyter in Open OnDemand
Click on the Jupyter app in Open OnDemand and choose your desired resources. Please ensure that you choose the Miniforge3 version of Jupyter.
Click launch at the bottom of the page to start a Jupyter Notebook session. You will be redirected to "My Interactive Sessions" where you can wait for the job to be allocated resources.
Once the job starts, click on Connect to Jupyter. This will open Jupyter in a new page in your browser.
For Jupyter versions < 7.0.0 please see below (for versions > 7.0.0, scroll down).
From here, click "new" and you should see the name of the ipykernel you created. Clicking on that will start a Jupyter notebook with a kernel that has access to all of the packages in your Conda environment.
For Jupyter versions > 7.0.0 please see below.
From here, click File > new > notebook. A new Jupyter notebook will open and a window will appear titled "Select Kernel". Click the drop down menu and under "Start Other Kernel" you should see the name of your Conda environment. Clicking on that will start your Jupyter notebook with a kernel that has access to all of the packages in your Conda environment.