Jupyter-Sapelo2: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
=== Version === | === Version === | ||
6.4.12, 6.5.2, 6.5.4, 6.5.6, 7.0.3, 7.2.0 | |||
=== Author / Distributor === | === Author / Distributor === | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
=== Running Program === | === Running Program === | ||
====Versions==== | |||
Please also refer to [[Running Jobs on Sapelo2]]. | Please also refer to [[Running Jobs on Sapelo2]]. | ||
*Jupyter | *Jupyter 6.4.12 is installed as part of Anaconda3 2022.10 with python 3.9.13. This version is installed at /apps/eb/Anaconda3/2022.10 | ||
*Jupyter 6.5.2 is installed as part of Anaconda3 2023.03-1 with python 3.10.9. This version is installed at /apps/eb/Anaconda3/2023.03-1 | |||
*Jupyter 6.5.4 is installed as part of Anaconda3 2023.09-0 with python 3.11.5. This version is installed at /apps/eb/Anaconda3/2023.09-0 | |||
*Jupyter 6.5.6 is installed as a module called JupyterNotebook/6.5.6-GCCcore-11.3.0 and it uses Python 3.10.4 | |||
*Jupyter 7.0.3 is installed as a module called JupyterNotebook/7.0.3-GCCcore-12.2.0 and it uses Python 3.10.8 | |||
*Jupyter | *Jupyter 7.2.0 is installed as a module called JupyterNotebook/7.2.0-GCCcore-13.2.0 and it uses Python 3.11.5 | ||
'''Please note: You do not have to install jupyter notebook on your local machine.''' | '''Please note: You do not have to install jupyter notebook on your local machine.''' | ||
To use Jupyter | To use Jupyter 6.4.12, please load the module: | ||
<pre class="gcommand" > | <pre class="gcommand"> | ||
module load Anaconda3/5. | module load Anaconda3/2022.10 | ||
</pre> | |||
To use Jupyter 6.5.2, please load the module: | |||
<pre class="gcommand"> | |||
module load Anaconda3/2023.03-1 | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
To use Jupyter 6.5.4, please load the module: | |||
<pre class="gcommand"> | |||
module load Anaconda3/2023.09-0 | |||
</pre> | |||
To use Jupyter 5.6 | To use Jupyter 6.5.6, please load the module: | ||
<pre class="gcommand" > | <pre class="gcommand"> | ||
module load | module load JupyterNotebook/6.5.6-GCCcore-11.3.0 | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
To use Jupyter 7.0.3, please load the module: | |||
<pre class="gcommand"> | |||
module load JupyterNotebook/7.0.3-GCCcore-12.2.0 | |||
</pre> | |||
To use Jupyter | To use Jupyter 7.2.0, please load the module: | ||
<pre class="gcommand" > | <pre class="gcommand"> | ||
module load | module load JupyterNotebook/7.2.0-GCCcore-13.2.0 | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
| Line 80: | Line 102: | ||
--> | --> | ||
====To use Jupyter notebook on sapelo2 with an interactive job==== | There are three options to use Jupyter notebook on Sapelo2. | ||
====Option 1: Use the Jupyter notebook interactive app in the Open OnDemand interface (highly recommended)==== | |||
The best way to run a Jupyter notebook on Sapelo2 is using the Jupyter notebook interactive app in the [[OnDemand]] interface to Sapelo2. | |||
<u>Some Important Notes about requesting resources for a Jupyter Notebook session through Open OnDemand:</u> | |||
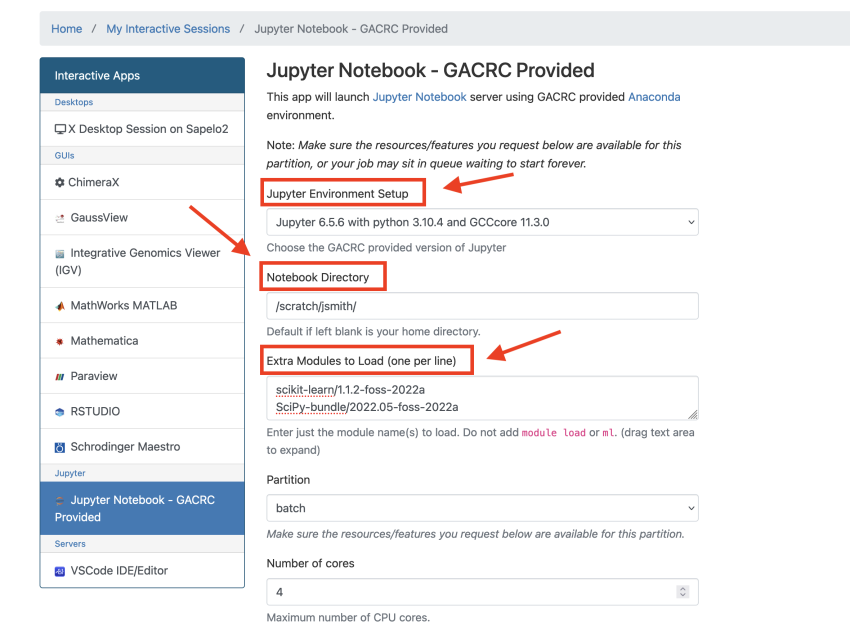
* With this option, you are able to use jupyter-notebook from centrally installed Anaconda3 modules or centrally installed JupyterNotebook modules, which you can choose under "Jupyter Environment Setup". | |||
* You can also choose which directory to start Jupyter from using the "Notebook Directory" option | |||
** For example, if you put /scratch/MyID in that box, it will start your session from your scratch dir and you will only have access to the files and folders there. | |||
** If you want to be able to access files in multiple directories (like both /home/MyID and /scratch/MyID) in one Jupyter session, you can set the starting Notebook Directory to simply / (root) which will allow you to access all of your directories. | |||
* You are also able to load other modules before launching the Jupyter Notebook with "Extra Modules to Load". Please ensure that the modules you load here are compatible with the toolchain and Python version selected in the "Jupyter Environment Setup" | |||
* The rest of the options are similar to the resources you would request in a normal job submission script (number of cores, time, memory, etc). | |||
[[File:OOD_JupyterNotebook_example.png|alt=|border|850x850px]] | |||
If you would like to use /lscratch for your jupyter notebook, open a Terminal in the jupyter notebook and there you can create an /lscratch/$USER directory and copy files to it. If you use /lscratch for your jupyter session, remember to copy any files you need to keep back to /scratch before closing this application. | |||
To add a Conda environment to Jupyter Notebook please see [[Using a Conda environment in Jupyter]] | |||
==== Option 2: Use the Jupyter notebook in an X Desktop session in the Open OnDemand interface==== | |||
Another option to run jupyter-notebook from the Open OnDemand interface is to first start an X Desktop session in the [[OnDemand]] interface and run jupyter-notebook from that desktop. This option is helpful if | |||
you would like to use a jupyter-notebook that is not installed as a central module, for example, one that is installed in a conda environment in the user's home dir. | |||
Steps to follow: | |||
*2.1: Open a browser on your local machine and point it to https://ondemand.gacrc.uga.edu (if accessing from off-campus, please connect to the UGA VPN first). Authenticate with UGA's SSO.* | |||
*2.2: Start an X Desktop session on Sapelo2, choose the resources to use (e.g. number of cores, memory, walltime, partition, gres, etc) and click Launch. | |||
*2.3: Once the session starts, click on "Launch X Desktop Session on Sapelo2" | |||
*2.4: In the X Desktop session, click on the Terminal icon in the panel at the bottom to start a Terminal session on the compute node allocated to your job. | |||
*2.5: If you would like to use /lscratch for your jupyter notebook, from the Terminal you can create an /lscratch/$USER directory and copy files to it. | |||
*2.6: In the Terminal, load any modules you want to use and/or activate a conda environment, if using jupyter-notebook from a conda environment. For example, if you would like to use the central module JupyterNotebook/6.5.6-GCCcore-11.3.0, you could load it with | |||
<pre class="gcommand"> | |||
ml JupyterNotebook/6.5.6-GCCcore-11.3.0 | |||
</pre> | |||
You can also load other modules that are compatible with this one (in the example above, you could load other modules that use the GCCcore-11.3.0, GCC-11.3.0, gompi-2022a, or foss-2022a toolchains). | |||
*2.7: Start jupyter-notebook in the Terminal with | |||
<pre class="gcommand"> | |||
NOTEBOOKPORT=8888 | |||
jupyter-notebook --port $NOTEBOOKPORT --no-browser | |||
</pre> | |||
where NOTEBOOKPORT should be set to some random value between 8000 and 10000. The example above uses 8888, but please choose a different value. | |||
In the terminal you should see some output ending with something like this: | |||
<pre class="gcommand"> | |||
[I 09:26:53.882 NotebookApp] Jupyter Notebook 6.4.12 is running at: | |||
[I 09:26:53.882 NotebookApp] http://10.2.1.91:8999/?token=83da4f2fb1f7f95bba6ba1e6d4d6ce5c81cadc09a602c811 | |||
[I 09:26:53.883 NotebookApp] or http://127.0.0.1:8999/?token=83da4f2fb1f7f95bba6ba1e6d4d6ce5c81cadc09a602c811 | |||
[I 09:26:53.883 NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation). | |||
[C 09:26:53.887 NotebookApp] | |||
To access the notebook, open this file in a browser: | |||
file:///home/shtsai/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/nbserver-1942279-open.html | |||
Or copy and paste one of these URLs: | |||
http://10.2.1.91:8999/?token=83da4f2fb1f7f95bba6ba1e6d4d6ce5c81cadc09a602c811 | |||
or http://127.0.0.1:8999/?token=83da4f2fb1f7f95bba6ba1e6d4d6ce5c81cadc09a602c811 | |||
</pre> | |||
*2.8: Start another Terminal in the X Desktop session and in it start firefox with | |||
<pre class="gcommand"> | |||
/apps/eb/Firefox/120.0.1/firefox | |||
</pre> | |||
*2.9: In the firefox browser that opens in your X Desktop session, paste the html file listed in the output of the jupyter-notebook command. In the example above the line is | |||
'''file:///home/shtsai/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/nbserver-1942279-open.html'''. This should open the jupyter notebook. | |||
*2.10: If you use /lscratch for your jupyter session, remember to copy any files you need to keep back to /scratch before closing this X Desktop session. | |||
To add a Conda environment to Jupyter Notebook please see [[Using a Conda environment in Jupyter]] | |||
====Option 3: To use Jupyter notebook on sapelo2 with an interactive job==== | |||
'''The port number for the jupyter notebook server should be some random value between 8000 and 10000. Assign this value to the variable 'NOTEBOOKPORT' in the submission script below replacing 8888. Please do not use 8888. If more than one person uses that same value you cannot establish the ssh tunnel''' | '''The port number for the jupyter notebook server should be some random value between 8000 and 10000. Assign this value to the variable 'NOTEBOOKPORT' in the submission script below replacing 8888. Please do not use 8888. If more than one person uses that same value you cannot establish the ssh tunnel''' | ||
Sample steps to use jupyter 6. | Sample steps to use jupyter 6.4.12, once you connect to sapelo2: | ||
<pre class="gcommand" > | <pre class="gcommand"> | ||
interact [OPTIONS] | |||
NOTEBOOKPORT=8888 | NOTEBOOKPORT=8888 | ||
| Line 96: | Line 201: | ||
echo "IPUSED is " $IPUSED | echo "IPUSED is " $IPUSED | ||
module load Anaconda3/ | module load Anaconda3/2022.10 | ||
jupyter-notebook --port $NOTEBOOKPORT --ip=$IPUSED --no-browser | jupyter-notebook --port $NOTEBOOKPORT --ip=$IPUSED --no-browser | ||
| Line 103: | Line 208: | ||
After running the steps above, establish a another ssh tunnel from your desktop or laptop to sapelo2 login node at port NOTEBOOKPORT. | After running the steps above, establish a another ssh tunnel from your desktop or laptop to sapelo2 login node at port NOTEBOOKPORT. | ||
'''For Mac/Linux Users''' | |||
If you are using a Linux or Apple machine for your desktop or laptop you can use the following command to establish the ssh tunnel | If you are using a Linux or Apple machine for your desktop or laptop you can use the following command to establish the ssh tunnel | ||
'''Make sure you replace NOTEBOOKPORT and IPUSED below with the port number and the IP address you are using ''' (see the output of the '''echo''' commands above) | '''Make sure you replace NOTEBOOKPORT and IPUSED below with the port number and the IP address you are using ''' (see the output of the '''echo''' commands above) | ||
<pre class="gcommand" > | <pre class="gcommand"> | ||
ssh -N -L NOTEBOOKPORT:IPUSED:NOTEBOOKPORT username@sapelo2.gacrc.uga.edu | ssh -N -L NOTEBOOKPORT:IPUSED:NOTEBOOKPORT username@sapelo2.gacrc.uga.edu | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Unless you have ssh key configured, you will be prompted for your MyID password and for Archpass Duo authentication. Once authentication is established, this session prompt will hang and you are ready to go to the next step. | Unless you have ssh key configured, you will be prompted for your MyID password and for Archpass Duo authentication. Once authentication is established, this session prompt will hang and you are ready to go to the next step. | ||
'''For Windows Users''' | |||
If you are using a Windows machine for your desktop or laptop download the '''[https://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/latest/x86/plink.exe plink program]''' to use in place of the ssh client. | If you are using a Windows machine for your desktop or laptop download the '''[https://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/latest/x86/plink.exe plink program]''' to use in place of the ssh client. | ||
The command for windows would be as follows: | The command for windows would be as follows: | ||
Assuming the plink.exe is in the current directory where you have a command window open. | Assuming the plink.exe is in the current directory where you have a command window open. | ||
'''Make sure you replace NOTEBOOKPORT and IPUSED below with the port number and the IP address you are using ''' (see the output of the '''echo''' commands above) | '''Make sure you replace NOTEBOOKPORT and IPUSED below with the port number and the IP address you are using ''' (see the output of the '''echo''' commands above) | ||
<pre class="gcommand" > | <pre class="gcommand"> | ||
plink -ssh -N -L NOTEBOOKPORT:IPUSED:NOTEBOOKPORT username@sapelo2.gacrc.uga.edu | plink -ssh -N -L NOTEBOOKPORT:IPUSED:NOTEBOOKPORT username@sapelo2.gacrc.uga.edu | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 126: | Line 233: | ||
Once you establish the ssh tunnel by running the command above you can access the Jupyter notebook by going to '''http://localhost:NOTEBOOKPORT''' using the browser on your desktop or laptop (make sure you replace NOTEBOOKPORT with the port number you used in the qlogin session). If the page displayed on the browser asks for a token or password, you can check the token shown in your qlogin session and copy and paste it into the token field in the page displayed in your browser. For example, the qlogin terminal might show something like this: | Once you establish the ssh tunnel by running the command above you can access the Jupyter notebook by going to '''http://localhost:NOTEBOOKPORT''' using the browser on your desktop or laptop (make sure you replace NOTEBOOKPORT with the port number you used in the qlogin session). If the page displayed on the browser asks for a token or password, you can check the token shown in your qlogin session and copy and paste it into the token field in the page displayed in your browser. For example, the qlogin terminal might show something like this: | ||
<pre class="gcommand" > | <pre class="gcommand"> | ||
[I 11:16:00.939 NotebookApp] JupyterLab extension loaded from /apps/eb/Anaconda3/2022.10/lib/python3.7/site-packages/jupyterlab | |||
[I | [I 11:16:00.939 NotebookApp] JupyterLab application directory is /apps/eb/Anaconda3/2022.10/share/jupyter/lab | ||
[I 11:16:00.942 NotebookApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: /home/zhuofei | |||
[I 11:16:00.942 NotebookApp] The Jupyter Notebook is running at: | |||
[I | [I 11:16:00.942 NotebookApp] http://10.2.1.30:8888/?token=857f8a9f63cf42f698ac1845db64219516a23e248019cdeb | ||
[I | [I 11:16:00.942 NotebookApp] or http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=857f8a9f63cf42f698ac1845db64219516a23e248019cdeb | ||
[I | [I 11:16:00.942 NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation). | ||
[I | [C 11:16:00.947 NotebookApp] | ||
[I | |||
[C | |||
To access the notebook, open this file in a browser: | |||
file:///home/zhuofei/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/nbserver-14353-open.html | |||
http://10. | Or copy and paste one of these URLs: | ||
http://10.2.1.30:8888/?token=857f8a9f63cf42f698ac1845db64219516a23e248019cdeb | |||
or http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=857f8a9f63cf42f698ac1845db64219516a23e248019cdeb | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Copy and paste the token, which in the example above is | Copy and paste the token, which in the example above is 857f8a9f63cf42f698ac1845db64219516a23e248019cdeb, into the proper field in the page displayed in your browser. | ||
=== Documentation === | ===Documentation=== | ||
Details at https://jupyter.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html | Details at https://jupyter.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html | ||
=== System === | ===System=== | ||
64-bit Linux | 64-bit Linux | ||
Latest revision as of 11:33, 8 October 2024
Category
Programming
Program On
Sapelo2
Version
6.4.12, 6.5.2, 6.5.4, 6.5.6, 7.0.3, 7.2.0
Author / Distributor
Description
"The Jupyter Notebook is a web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and explanatory text" Jupyter
Running Program
Versions
Please also refer to Running Jobs on Sapelo2.
- Jupyter 6.4.12 is installed as part of Anaconda3 2022.10 with python 3.9.13. This version is installed at /apps/eb/Anaconda3/2022.10
- Jupyter 6.5.2 is installed as part of Anaconda3 2023.03-1 with python 3.10.9. This version is installed at /apps/eb/Anaconda3/2023.03-1
- Jupyter 6.5.4 is installed as part of Anaconda3 2023.09-0 with python 3.11.5. This version is installed at /apps/eb/Anaconda3/2023.09-0
- Jupyter 6.5.6 is installed as a module called JupyterNotebook/6.5.6-GCCcore-11.3.0 and it uses Python 3.10.4
- Jupyter 7.0.3 is installed as a module called JupyterNotebook/7.0.3-GCCcore-12.2.0 and it uses Python 3.10.8
- Jupyter 7.2.0 is installed as a module called JupyterNotebook/7.2.0-GCCcore-13.2.0 and it uses Python 3.11.5
Please note: You do not have to install jupyter notebook on your local machine.
To use Jupyter 6.4.12, please load the module:
module load Anaconda3/2022.10
To use Jupyter 6.5.2, please load the module:
module load Anaconda3/2023.03-1
To use Jupyter 6.5.4, please load the module:
module load Anaconda3/2023.09-0
To use Jupyter 6.5.6, please load the module:
module load JupyterNotebook/6.5.6-GCCcore-11.3.0
To use Jupyter 7.0.3, please load the module:
module load JupyterNotebook/7.0.3-GCCcore-12.2.0
To use Jupyter 7.2.0, please load the module:
module load JupyterNotebook/7.2.0-GCCcore-13.2.0
There are three options to use Jupyter notebook on Sapelo2.
Option 1: Use the Jupyter notebook interactive app in the Open OnDemand interface (highly recommended)
The best way to run a Jupyter notebook on Sapelo2 is using the Jupyter notebook interactive app in the OnDemand interface to Sapelo2.
Some Important Notes about requesting resources for a Jupyter Notebook session through Open OnDemand:
- With this option, you are able to use jupyter-notebook from centrally installed Anaconda3 modules or centrally installed JupyterNotebook modules, which you can choose under "Jupyter Environment Setup".
- You can also choose which directory to start Jupyter from using the "Notebook Directory" option
- For example, if you put /scratch/MyID in that box, it will start your session from your scratch dir and you will only have access to the files and folders there.
- If you want to be able to access files in multiple directories (like both /home/MyID and /scratch/MyID) in one Jupyter session, you can set the starting Notebook Directory to simply / (root) which will allow you to access all of your directories.
- You are also able to load other modules before launching the Jupyter Notebook with "Extra Modules to Load". Please ensure that the modules you load here are compatible with the toolchain and Python version selected in the "Jupyter Environment Setup"
- The rest of the options are similar to the resources you would request in a normal job submission script (number of cores, time, memory, etc).
If you would like to use /lscratch for your jupyter notebook, open a Terminal in the jupyter notebook and there you can create an /lscratch/$USER directory and copy files to it. If you use /lscratch for your jupyter session, remember to copy any files you need to keep back to /scratch before closing this application.
To add a Conda environment to Jupyter Notebook please see Using a Conda environment in Jupyter
Option 2: Use the Jupyter notebook in an X Desktop session in the Open OnDemand interface
Another option to run jupyter-notebook from the Open OnDemand interface is to first start an X Desktop session in the OnDemand interface and run jupyter-notebook from that desktop. This option is helpful if you would like to use a jupyter-notebook that is not installed as a central module, for example, one that is installed in a conda environment in the user's home dir.
Steps to follow:
- 2.1: Open a browser on your local machine and point it to https://ondemand.gacrc.uga.edu (if accessing from off-campus, please connect to the UGA VPN first). Authenticate with UGA's SSO.*
- 2.2: Start an X Desktop session on Sapelo2, choose the resources to use (e.g. number of cores, memory, walltime, partition, gres, etc) and click Launch.
- 2.3: Once the session starts, click on "Launch X Desktop Session on Sapelo2"
- 2.4: In the X Desktop session, click on the Terminal icon in the panel at the bottom to start a Terminal session on the compute node allocated to your job.
- 2.5: If you would like to use /lscratch for your jupyter notebook, from the Terminal you can create an /lscratch/$USER directory and copy files to it.
- 2.6: In the Terminal, load any modules you want to use and/or activate a conda environment, if using jupyter-notebook from a conda environment. For example, if you would like to use the central module JupyterNotebook/6.5.6-GCCcore-11.3.0, you could load it with
ml JupyterNotebook/6.5.6-GCCcore-11.3.0
You can also load other modules that are compatible with this one (in the example above, you could load other modules that use the GCCcore-11.3.0, GCC-11.3.0, gompi-2022a, or foss-2022a toolchains).
- 2.7: Start jupyter-notebook in the Terminal with
NOTEBOOKPORT=8888 jupyter-notebook --port $NOTEBOOKPORT --no-browser
where NOTEBOOKPORT should be set to some random value between 8000 and 10000. The example above uses 8888, but please choose a different value.
In the terminal you should see some output ending with something like this:
[I 09:26:53.882 NotebookApp] Jupyter Notebook 6.4.12 is running at:
[I 09:26:53.882 NotebookApp] http://10.2.1.91:8999/?token=83da4f2fb1f7f95bba6ba1e6d4d6ce5c81cadc09a602c811
[I 09:26:53.883 NotebookApp] or http://127.0.0.1:8999/?token=83da4f2fb1f7f95bba6ba1e6d4d6ce5c81cadc09a602c811
[I 09:26:53.883 NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).
[C 09:26:53.887 NotebookApp]
To access the notebook, open this file in a browser:
file:///home/shtsai/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/nbserver-1942279-open.html
Or copy and paste one of these URLs:
http://10.2.1.91:8999/?token=83da4f2fb1f7f95bba6ba1e6d4d6ce5c81cadc09a602c811
or http://127.0.0.1:8999/?token=83da4f2fb1f7f95bba6ba1e6d4d6ce5c81cadc09a602c811
- 2.8: Start another Terminal in the X Desktop session and in it start firefox with
/apps/eb/Firefox/120.0.1/firefox
- 2.9: In the firefox browser that opens in your X Desktop session, paste the html file listed in the output of the jupyter-notebook command. In the example above the line is
file:///home/shtsai/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/nbserver-1942279-open.html. This should open the jupyter notebook.
- 2.10: If you use /lscratch for your jupyter session, remember to copy any files you need to keep back to /scratch before closing this X Desktop session.
To add a Conda environment to Jupyter Notebook please see Using a Conda environment in Jupyter
Option 3: To use Jupyter notebook on sapelo2 with an interactive job
The port number for the jupyter notebook server should be some random value between 8000 and 10000. Assign this value to the variable 'NOTEBOOKPORT' in the submission script below replacing 8888. Please do not use 8888. If more than one person uses that same value you cannot establish the ssh tunnel
Sample steps to use jupyter 6.4.12, once you connect to sapelo2:
interact [OPTIONS] NOTEBOOKPORT=8888 IPUSED=$(hostname -i) echo "NOTEBOOKPORT is " $NOTEBOOKPORT echo "IPUSED is " $IPUSED module load Anaconda3/2022.10 jupyter-notebook --port $NOTEBOOKPORT --ip=$IPUSED --no-browser
After running the steps above, establish a another ssh tunnel from your desktop or laptop to sapelo2 login node at port NOTEBOOKPORT.
For Mac/Linux Users
If you are using a Linux or Apple machine for your desktop or laptop you can use the following command to establish the ssh tunnel
Make sure you replace NOTEBOOKPORT and IPUSED below with the port number and the IP address you are using (see the output of the echo commands above)
ssh -N -L NOTEBOOKPORT:IPUSED:NOTEBOOKPORT username@sapelo2.gacrc.uga.edu
Unless you have ssh key configured, you will be prompted for your MyID password and for Archpass Duo authentication. Once authentication is established, this session prompt will hang and you are ready to go to the next step.
For Windows Users
If you are using a Windows machine for your desktop or laptop download the plink program to use in place of the ssh client. The command for windows would be as follows: Assuming the plink.exe is in the current directory where you have a command window open.
Make sure you replace NOTEBOOKPORT and IPUSED below with the port number and the IP address you are using (see the output of the echo commands above)
plink -ssh -N -L NOTEBOOKPORT:IPUSED:NOTEBOOKPORT username@sapelo2.gacrc.uga.edu
Once you establish the ssh tunnel by running the command above you can access the Jupyter notebook by going to http://localhost:NOTEBOOKPORT using the browser on your desktop or laptop (make sure you replace NOTEBOOKPORT with the port number you used in the qlogin session). If the page displayed on the browser asks for a token or password, you can check the token shown in your qlogin session and copy and paste it into the token field in the page displayed in your browser. For example, the qlogin terminal might show something like this:
[I 11:16:00.939 NotebookApp] JupyterLab extension loaded from /apps/eb/Anaconda3/2022.10/lib/python3.7/site-packages/jupyterlab
[I 11:16:00.939 NotebookApp] JupyterLab application directory is /apps/eb/Anaconda3/2022.10/share/jupyter/lab
[I 11:16:00.942 NotebookApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: /home/zhuofei
[I 11:16:00.942 NotebookApp] The Jupyter Notebook is running at:
[I 11:16:00.942 NotebookApp] http://10.2.1.30:8888/?token=857f8a9f63cf42f698ac1845db64219516a23e248019cdeb
[I 11:16:00.942 NotebookApp] or http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=857f8a9f63cf42f698ac1845db64219516a23e248019cdeb
[I 11:16:00.942 NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).
[C 11:16:00.947 NotebookApp]
To access the notebook, open this file in a browser:
file:///home/zhuofei/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/nbserver-14353-open.html
Or copy and paste one of these URLs:
http://10.2.1.30:8888/?token=857f8a9f63cf42f698ac1845db64219516a23e248019cdeb
or http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=857f8a9f63cf42f698ac1845db64219516a23e248019cdeb
Copy and paste the token, which in the example above is 857f8a9f63cf42f698ac1845db64219516a23e248019cdeb, into the proper field in the page displayed in your browser.
Documentation
Details at https://jupyter.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html
System
64-bit Linux